NUMBERS
What is numbers?
Numbers are symbols or words which represent quality of something for example in form 1B there are forty four students.
i.e. 44 students
The numbers are represented by symbols called numerals.
Each symbol in a numeral is called a digit.
E.g. in 256 there are three digits which are 2, 5, and 6.
There are ten digits which are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9
Each digit in a numeral has a value called place value.
Example in 316, 6 is called ones and can be written 6x1, 1is called tens and can be written 1x10 and 3 is called hundreds and can be written 3x100.
Therefore 316 can be written as 3x100+1x10+6x1 this form is called expanded form.
The system where numbers are in groups of ten is called base ten numerations or decimal system numeration. The place value of every digit in decimal system numeration is ten times the place value of the next to the right.
Table of place values;
Exercise 1.1
1. Write each of the following numbers in expanded form;-
a. 94=
b. 7019=
c. 50=
d. 303
e. 5003=
f. 500=
g. 999=
h. 5=
i. 5000=
2. Find the place value of the following;-
a. 513 (1)
The place value of 1 is
b. 357999 (5)
The place value of 5 is
c. 50149 (5)
The place value of 5 is
d. 8665 (8)
The place value of 8 is
e. 227 (7)
The place value of 7 is
f. 900412 (4)
The place value of 4 is
3. Write the numerals for each of the following;-
i. 9x100+0x10+1x1
ii. 5x10000+5x1000+5x100+5x10+5x1
iii. 6x100000+8x10000+0x1000+1x100+7x10+0x1
iv. 5x100+0x10+1x1
NATURAL AND WHOLE NUMBERS
Natural numbers
Natural numbers are the ones that begin with 1, 2, 3 to infinity.
They are counting number, they denoted by N
Number line of natural numbers.
Whole numbers
Are the ones that begin by 0, 1, 2, 3, to infinity? They are denoted by W, in a number line.
Even, odd and prime numbers;-
Even;- are natural numbers which are divisible by 2 without remainder.
Example; - 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12.
Odd;- are natural numbers which are not divisible by 2, when they are divided by 2 they give remainder, so the answer is not a natural numbers.
Example; - 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11……………………….
Prime numbers;-
Prime numbers are natural numbers which are divisible by one and by themselves. They are the ones with only two factors.
Example;- 2, 3, 5, 11, 13…………………
Numbers up to one billion
Exercise 1.2
1. For the given numbers below, write down which are;-
a) Even b) Prime c) Odd
9, 12, 15, 17, 25, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71.
2. Write down the prime numbers between 70 and 90.
3. Write down a number which is even and prime.
4. Among the numbers 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13. What is not a prime number?
5. Show even, odd, and prime numbers less than 10 on separate number.
6. (a) Given any point as a number on a number line for N or W. Can you always name another one to the right of it?
7. Given any two points as numbers one after another on a number line for N or W. Can you find the whole numbers between them?
8. Do the points representing N and W on a number line completely fill the number line?
9. How does N differ from W?
More examples
1. Write the following numerals in words;-
a. 72 –Seventy two
b. 10368 – Ten thousand three hundred and sixty eight
c. 1152 – One thousand one hundred and fifty two
d. 144 – One hundred and forty four
e. 57392 – Five hundred and seventy three thousand nine hundred and twenty one
f. 952675 – Nine hundred and fifty two thousand six hundred and seventy five
g. 105,451,225 – One hundred and five million four hundred and fifty one thousand two hundred and twenty five
2. Express the statement in numerals;-
Nine billion eight hundred million and two hundred =9,800,000,200
3. Write down the largest four digit number = 9,999
4. Write down the largest four digit number when the digits are not repeating =9876
5. Write down the smallest three – digit number without using a zero =111
6. Change the order of the digits in 47986 to make;
a. The largest possible number = 98764
b. The smallest possible number = 46789
7. Write down the number with 6 in the hundred place, 9 in the tens place, 0 in the thousands place, 4 in the units place and 3 in the ten thousands place.
30, 694
8. Write down next three counting numbers after 6999.
7000, 7001, 7002
9. Write the numbers in words;-
a. 6054 – Six thousand and fifty four
b. 3,250,000 – Three million two hundred and fifty thousand
c. 106,000 – One hundred and six thousand
d. 100,006 – One hundred thousand and six
e. 205,020 – Two hundred and five thousand and twenty
f. 2,415,982,728 – Two billion, four hundred and fifteen million, nine hundred and eighty two thousand, seven hundred and twenty eight.
10. Write in numerals;-
a. Six hundred seventy five =675
b. Four hundred and five =405
c. Three thousand and sixteen =316
d. Eight thousand and sixteen =8016
e. One hundred thirty seven thousand two hundred and fourteen =137214
f. One million five hundred thousand =1,500,000
g. Two million twenty three =2,000,023
h. Nineteen thousand and forty five =19,045
i. One billion fourteen million two hundred and fifteen thousand =1,014,215,000
Operations with whole numbers;-
These are four operations which are addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Addition (plus)(+)
Horizontal addition
E.G. 254+369=623
14796+230+14=15030
Vertical addition
The answer obtained after adding is called sum.
Subtraction (-) (minus);-
Horizontal subtraction
E.g. 2349610 – 1396789 = 952821
129 – 98 =31
Vertical subtraction;-
The answer obtained after subtracting numbers is called Difference.
Multiplication/Times (x)
a x b = c
a = Multiplicant
b = Multiplier
c = Product
There are two types of Multiplication
Horizontal multiplication
E.g. 2486 x 7 = 17402
126 x 8 = 1008
Vertical multiplication
The number that multiples is called multiplier
The number to be multiplied is called multiplicand
The answer obtained after multiplication is called product.
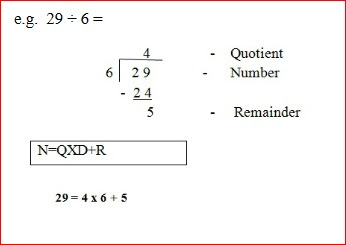
Division (÷)
a ÷ b = c
a = dividend
b = divisor
c = quotient
Short division

Long or vertical division

The number that divides is called divisor
The number to be divided is called dividend
The answer obtained after division is called Quotient
The left over upon division is called Remainder
 Word problems on whole numbers
Word problems on whole numbers
1. E.g. In a school garden there are four rows of cabbage with 12 in each row, six rows of tomatoes with eight in each row. How many plants of each kind are there?
Solution;-
1row = 12cabbage
4rows = x
X = 12 cabbages x 4 rows
X = 48 cabbages
1row = 8 tomatoes
6rows = x
X = 8 tomatoes x 6rows
X = 48 tomatoes
There are 48 cabbages plants and
48 tomatoes plants
2. Two thousand four hundred shillings are deposited by a teacher each month, how much is this this after two years?
Solution;-
2400 shs = 1 month
1 year = 12 months
2 years = 24 months
2400 shs x 24 months
576000/=
More examples
1. 324 + 1984
Solution;-
324
+1984
2308
2. 28782-2784+294
Solution;-
28782
-2784
25998
+ 294
26292
3. 2479249872
-944129872
1535120000
Will the sums of the following be even or odd;-
4. Two numbers which are Odd.
The answer must be even.
5. Two numbers which are even.
Even numbers
6. An odd and even number
Odd numbers
7. Any two odd numbers
Even numbers
8. Use horizontal way to find products in questions;-
1. 128 x 5 =640
2. 195 x 9 =1755
3. 17289 x 2 = 34578
9. Use long multiplication method to evaluate;-
249752 x 8921
Solution;-

10. Find the product and quotient of the following
a) 247 X 100
Solution;-
247
x100
000
000
+ 247
24700
b) 4000 ÷ 100
Solution;-

Revision exercise
1. In a school garden there are 4 rows of carrots with 10 in each row.
2. Six students were given 96,000 shillings to share equally. How many shillings did each student get
3. The cost of one kilogram of sugar is 700 shillings and juma buys 8 kgs of sugar. How much did cost him?
4. Richard sold 240 copies of the daily newspaper for 300 shillings each, 198 pieces of the uhuru newspaper for 200 shillings and 6 sports magazine for 500 shillings each. How much did he collect in all?
5. There are 17 streams in a school, each stream has 35 pupils. How many pupils are there in the school?
6. A page of a book has 36 lines. If each line contains 14 words, how many words are these if the book has 250 pages?
7. Jim’s school is 13 km from his home. If he goes to school daily how many kilometers does he travel in 196 days?
8. Each day a school shop collects sh. 75000 from the customers. If the collection was made for eight days and sh. 275000 of the collected money was used to make a fence for the school. How much money was left?
9. A school collects 140 eggs from its poultry farm each day. Each egg costs 80shillings. How much money per day does the school earn in selling the eggs?
10. A school of 900 students has decided to make uniforms for each student. If a shirt and a pair of trousers need 2 m and 1.5 m respective, how much of each material of cloth will the school need so as to give uniforms to all students?
SOLUTIONS
Qn 1.
4 rows @ 10 plants
4 x10 = Total plants
40
There are 40 carrot plants.
Qn 2.
6 students = 96000 shillings
96000 ÷ 6 =16000
Each student got 16000shs
Qn 3.
1kg = 700shs
Juma buys 8 kgs
700 x 8= 5600
It costed him 5600/=
Qn 4.
240 x 300 =72000
198 x 200 =39600
6 x 500 =3000
72000 + 39600 + 3000 =114600
He got 114,600/=
Qn 5.
17 streams x 35 pupils
17 x 35 = 595
Therefore the total number of pupils in the school is 595.
Qn 6.
36 lines x 14 words
36 x 14 = 504 x 250 pages
126,000 words
Qn 7.
1 day = 26 km
196 days = ? km
196 x 26 =?
5096 kms
He travel 5096 km
Qn 8.
8 days = 75000 x 8
600,000/=
600,000
-275,000
325,000
325,000/= was left.
Qn 9.
Each egg costs = 80 shillings
Each day 140 eggs
We multiply 140 x 80
=112000
The school earns 112000 each day
Qn 10.
900 x 2 m = 1800m
900 x 1.5 = 1350m
The school will need 1800m and 1350m respectively.
ORDER OF OPERATIONS
The order of priority is often given by the word BODMAS to mean
B rackets
O rders
M ultiplication
A ddition
S ubtraction
So first perform any operation in brackets, then any use of orders division or multiplication followed by addition or subtraction.
Example; evaluate the following
a. 12 + 4 x 2 = 12 + (4 x 2) = 12 + 8 = 20
b. 20 ÷ 2 + 3 = (20 ÷ 2) + 3 = 10 + 3 = 13
c. 4 x 3 + 7 x 2 = (4 x 3) + (7 x 2) =12 + 14 =26
1:4 FACTORS AND MULTIPLES OF NUMBERS
When a number divides exactly into another number, it is called a factor of a second number.
The second number is called a multiple of the first numbers.
Example; 16 ÷ 8 = 2 so 2 is the factor of 16 and 16 is the multiple of 2. Other factors of 16 are 8, 4, 1 and 16.
In general one (1) is a factor of every number and each number is a factor of itself.
- Factors of a number are numbers less than the given number.
- Factors are finite, and divisors of the given number.
- Multiple are number greater than the given number.
- They are infinite and dividend of a particular number.
E.g. factors of 36 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 36
Multiple of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 243, 729………………
PRIME FACTORIZATION
Is the process of writing numbers using their prime factors we use the short division in writing/factorization.
E.g. write the following as the product of their prime factors.

 THE LOWEST COMMON MULTIPLES (LCM)
THE LOWEST COMMON MULTIPLES (LCM)
LCM is the short form of lowest or least common multiple.
E.g. 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24 …………
3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 ……………………..
Common multiples are = (6, 12, 18 and 24)
LCM = 6
E.g. find the lowest common multiples of 9, 18, 24
Soln
9 = 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99, 108, 117, 126……….
18 = 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, 108, 126, 144, 162, 180, 198………………
27 = 27, 54, 81, 198, 135, 162, 189…………………………………
Common multiples are = {54, 108….}
The least common multiples = 54.
PROPERTIES OF WHOLE NUMBERS
There are five properties of whole numbers.
1. Closure property (law)
When two or more whole numbers are operated by adding or multiplying the answer is also a whole numbers.
That is if a and b are whole numbers. Then a + b = c. c is also a whole number. a x b = d d is also a whole number.
E.g. 4 + 6 = 10
3 + 5 = 15
2. Commutative property
If a and b are whole numbers.
Then (i) a + b = b + a
(ii) a x b = b x a
E.g. 3 + 4 = 7
4 + 3 = 7
Implies: 3 + 4 = 4 + 3
a + b = b + a
9 x 6 = 54
6 x 9 = 54
a x b = b x a
3. Association property
If a + b & c are whole number.
Then (i) (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
(ii) (a x b) c = a (b x c)
e.g. (2 + 3) + 4 = 5 + 4 = 9
2 + (3 + 4) = 2 + 7 =9
Implies: (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4)
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
e.g. (4 x 2) x 5 = 8 x 5 = 40
4 x (2 x 5) = 4 x 10 = 40
Implies: (4 x 2) x 5 = 4 x (2 x 5)
(a x b) c = a (b x c)
4. Distributive property
If a, b and c are whole numbers, then
a x (b + c) = (a x b) + (a x c)
E.g. 4 x (6 + 9) = 4 x 15 = 60
4 x (6 + 9) = (4 x 6) + (4 x 9)
= 24 + 36
= 60
5. Identity property
If a is a whole number,
Then (i) a + 0 = 0 + a = a
0 is called an identity of addition
(ii) a x 1 = 1 x a = a
1 is called and identity of multiplication.
Exercise 1:5
1. Match the property in group A and group B then name the property
Group A
(a) 2 + (3 + 5)
(b) 1 + (2 + 3)
(c) 2 + (2 + 1)
(d) 4 + (3 + 5)
(e) 1 + (1 + 3)
(f) 8 + (4 + 4)
(g) (1 + 3) + 1
Group B
(h) (2 + 3) + 5
(i) (2 + 2) + 1
(j) (8 + 4) + 4
(k) (1 + 2) + 3
(l) (3 + 5) + 4
(m) (1 + 1) + 3
(n) 1 + (1 + 3)
Solution
a and h have associative property
b and k have commutative property
c and l have associative property
e and m have commutative property
f and j have associative property
g and n have commutative property
2. By using properties of whole numbers given reasons why each of the following two expressions are equal
(a) 5 + (6 + 7) = (7 + 6) +5
- The answer to the two expressions will be the same because the numbers have commuted.
(b) (8 + 3) + 4 = 8 + (4 + 3)
- When you solve this you will get the same answer because of the exchange of the numbers.
(c) 5 + (2 + 1) = 1 + (3 + 2)
- In this expression, we have seen that they are two different expressions so you cannot get the same answer from the two.
(d) (5 + 3) + 2 = 3 + (2 + 5)
- In this two expression you can get the same answer because only the position of numbers and brackets as the one that has changed.
3. Telling / writing equal expressions;
(a) 2 x (5 x 3) = (2 x 5) x 3 – associative property
(b) 4 x (3 x 5) = (4 x 3) x 5 – associative property
(c) 2 x (4 x 7) = 7 x (2 x 4) – associative property
(d) 3 x (2 x 2) = 3 x (2 x 2) x 3 – commutative property
(e) (3 x 2) x 6 = 16 x (2 x 2) – commutative property
(f) (3 x 2) x 3 = (2 x 3) x 3 – commutative property
4. Why is it permitted to write 3 x 2 x 5 x 9 without any brackets?
Because even if they are written without brackets they don’t destroy the meaning of the question / statement.
5. Express each of the following in the form of (a x b) + (a x c)
(a) 2 x (3 + 5)
= (2 x 3) + (2 x 5)
(b) 4 x (3 + 10)
= (4 x 3) + (4 x 10)
(c) 2 x (3 + 7)
= (2 x 3) + (2 x 7)
(d) 4 x (3 + 1)
= (4 x 3) + (4 x 1)
6. Express each of the following in the form a x (b + c)
(a) (2 x 5) + (2 x 3)
= 2 x (5 + 3)
(b) (5 x 3) + (5 x 7)
= 5 x (3 + 7)
(c) (2 x 1) + (2 x 3)
= 2 x (1 + 3)
(d) (7 x 3) + (7 x 1)
= 7 x (3 + 1)
7. Calculate the following;
(a) 14 x 5 + 16 – 4 =82
(b) 36 x 72 ÷ 4 = 648
(c) (144 + 20) x 48 + 4 ÷ 2 = 7872
(d) 24 x (10 + 54) + 8 = 192
1:5 INTEGERS
The integers are whole numbers from negative infinity to positive infinity.
They are denoted by Z.
The order of the size of the number 1, 2, 3, 4…… can be represented as points on a number line.
Starting from 0 to the right and other numbers from 0 to the left
Number line for Z
If we want to know which number is larger than the other we have to consider which one is to the right or left?
Consider the following
E.g. write down all the integers between – 5 and 4
Solution
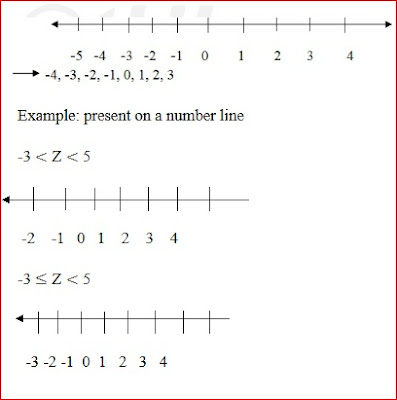 Operation with integers
Operation with integers
Integers can be operated using number lines except for division
Addition of integers
RULE 1: To add a negative integer you move to the left on the number line.
Example
-2 + -5 = -7
Start at -2 move 5 steps to the left or star at 0 move 2 steps to the left then -5 steps to the left
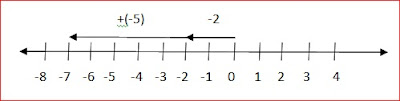
RULE 2: To add a positive integer you move to right on number line.
Example
 Subtraction of integers
Subtraction of integers
Subtraction of positive integers gives the same result as addition of integers.
RULE 1: To subtract a positive integer you move to the left on the number line.
 Multiplication
Multiplication
The rules for multiplying are as follows
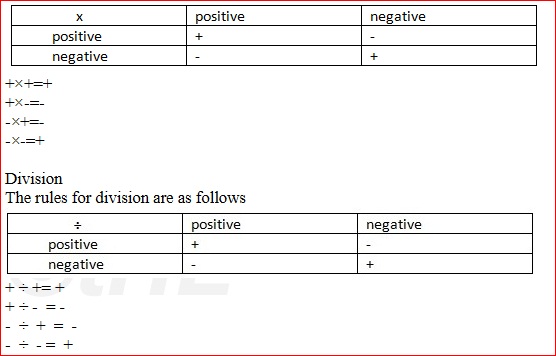
NOTE: The results are similar to the rules of multiplication.
Example
-36 ÷ 6 = -6
24 ÷ 6 = +4
24 ÷ -6 = -4
-24 ÷ 6 = -4
-24 ÷ -6 = 4


























































